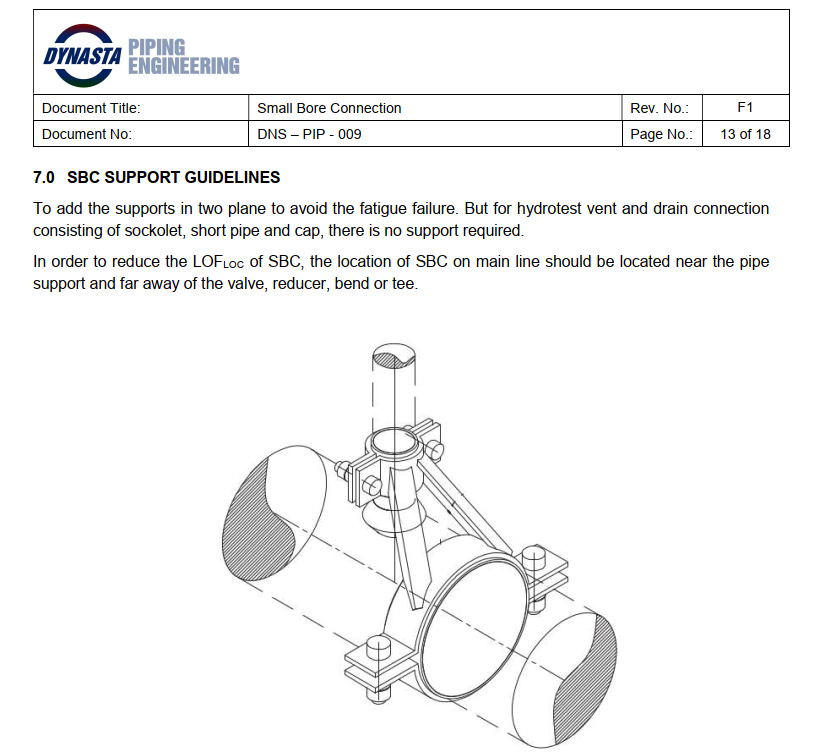
In piping stress analysis, distinguishing between Sustain Load Case and Alt Sustain is crucial for ensuring the safety and reliability of piping systems. Here's a quick breakdown:
Sustain Load Case
- What it is: Evaluates the piping system under constant, long-term primary loads during normal operation.
- Examples: Internal pressure, pipe weight (including fluid and insulation), and static forces from connected equipment.
- Purpose: Ensures the system can handle these sustained loads without failure or excessive deformation over its design life.
- Design Criteria: Stresses must comply with allowable limits (e.g., ASME B31.3).
Alt Sustain (Alternate Sustain)
- What it is: Evaluates the piping system under varying sustained loads representing different operating conditions.
- Examples: Different pressures, temperatures, or fluid densities during startup, normal operation, or shutdown.
- Purpose: Ensures the system can handle these alternate sustained loads without failure.
- Design Criteria: Similar to the sustain load case, stresses must meet code-specified allowable limits.

Key Takeaway
- Sustain Load Case: Focuses on constant, long-term loads during normal operation.
- Alt Sustain: Focuses on varying sustained loads during different operational scenarios.
Both load cases are critical for compliance with standards like ASME B31.3 and are typically analyzed using tools like CAESAR II. Understanding these concepts ensures the integrity and safety of piping systems under all operating conditions.
 DYNASTA
DYNASTA