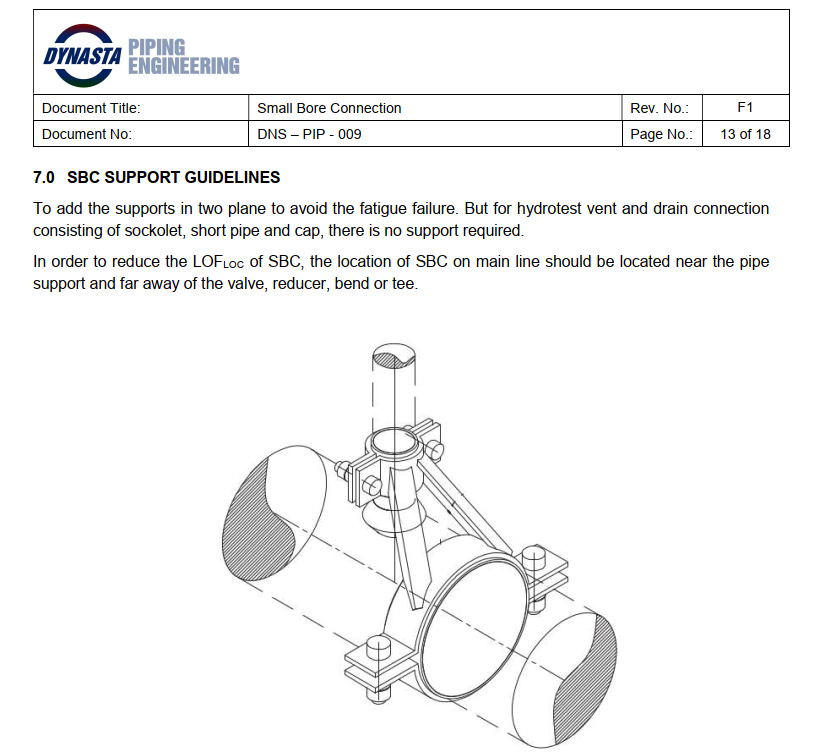
Introduction
Pipe stress analysis is a critical process in engineering to ensure the integrity, safety, and functionality of piping systems under various load conditions. This analysis helps to prevent failures due to excessive stress, thermal expansion, vibration, and external forces. A systematic workflow ensures that the analysis is performed efficiently and accurately, following industry standards such as ASME B31.3, B31.4, B31.8, and ISO 14692 for GRE/FRP piping.
Step 1: Define Project Scope and Input Data
• Identify the piping system and its operational requirements.
• Gather design specifications, including:
o Pipe material and properties
o Pipe size and wall thickness
o Fluid type, temperature, and pressure
o Piping layout and routing
o Support types and locations
o Equipment connection points
• Obtain relevant industry codes and standards.
Step 2: Establish Load Cases
• Define the different loading scenarios the piping system will experience:
o Internal pressure
o Thermal expansion and contraction
o Dead weight (pipe, fluid, insulation, etc.)
o External loads (seismic, wind, snow, etc.)
o Dynamic effects (water hammer, vibration, pulsation, etc.)
o Support and anchor movements
Step 3: Create the Piping Model
• Develop a 3D representation of the piping system using stress analysis software (e.g., CAESAR II, AutoPIPE, …).
• Input all material properties, geometric dimensions, and boundary conditions.
• Ensure accurate representation of supports, restraints, and flexibility components.
Step 4: Perform Preliminary Analysis
• Run an initial simulation to identify potential stress concentrations.
• Verify deflections, forces, and moments against allowable limits.
• Check for excessive flexibility or rigidity in the system.
Step 5: Optimize Support and Restraint Locations
• Adjust support spacing to control excessive sagging and displacement.
• Modify guide and anchor placements to manage thermal expansion forces.
• Incorporate expansion joints or loops where necessary.
• Ensure uniform stress distribution to avoid localized overloading.
Step 6: Perform Detailed Stress Analysis
• Conduct a comprehensive stress assessment under all defined load cases.
• Evaluate:
o Sustained stress (pressure and weight-related)
o Thermal stress (expansion/contraction effects)
o Occasional stress (seismic, wind, surge, etc.)
o Fatigue and cyclic stress effects
• Compare analysis results with allowable stress limits from applicable codes.
Step 7: Validate and Review Results
• Cross-check analysis outputs with engineering judgment and industry guidelines.
• Perform sensitivity analysis for different loading conditions.
• If necessary, re-run the analysis with modified supports or alternative routing.
Step 8: Document Findings and Recommendations
• Prepare a detailed stress analysis report including:
o Input data and assumptions
o Load cases and applied conditions
o Stress plots and deflection diagrams
o Compliance with applicable codes and standards
o Recommended design modifications (if any)
• Share results with project stakeholders for review and approval.
Step 9: Implement Design Modifications
• Incorporate necessary changes into the piping design based on analysis findings.
• Update piping layout, support locations, and expansion elements.
• Perform final verification to ensure compliance and system reliability.
Step 10: Field Testing and Validation
• Conduct hydrostatic pressure testing to confirm system integrity.
• Perform non-destructive testing (NDT) to detect any material defects.
• Ensure proper installation and alignment of supports and restraints.
Conclusion
Following a structured workflow for pipe stress analysis ensures that piping systems are designed to withstand operational loads while maintaining safety and compliance. By systematically defining load cases, optimizing supports, and validating results, engineers can enhance the longevity and reliability of piping networks in various industries. Continuous advancements in software and analytical techniques further refine the accuracy and efficiency of stress analysis processes.
 DYNASTA
DYNASTA